
Persian Alphabet and Numerals
Persian alphabet (الفبای فارسی / alefbā-ye fârsi) فارسی)
After the Islamic conquest of the Persian Sassanian Empire in 642 AD, Arabic became the language of government, culture and especially religion, and the Arabic alphabet was adapted to write the Persian language. This is now known as the Persian or Perso-Arabic alphabet (الفبای فارسی / alefbā-ye fârsi).
Notable features of Persian language
- Type of writing system: abjad - includes letters only for consonants. Vowels, when indicated, are written with diacritics and/or combinations of consonant letters
- Direction of writing: right to left in horizontal lines; numerals written from left to right.
- Used to write: Persian (فارسی)
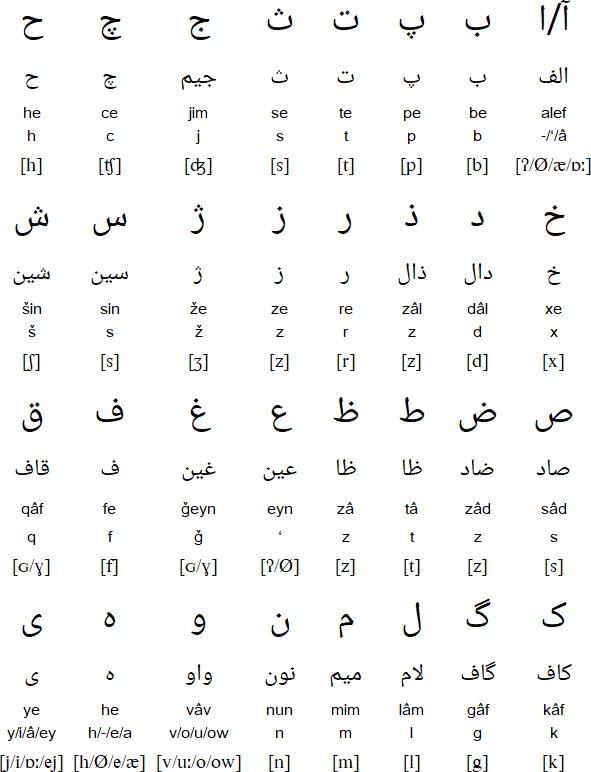
Notes
- Persian has six vowel sounds and two diphthongs: â (/ɒː/), a (/æ/), e (/e/), I (/iː/), o (/o/), u (/uː/), ey (/ej/) and ow (/ow/).
- "Alef" has no particular sound. At the beginning of words by means of diacritics it can denote "â" (آ), "a" (اَ), "e" (اِ), "o" (اُ) but elsewhere, it always denotes "â". However, only the diacritic of "â" (آ) is commonly written and you just have to memorize the pronunciation. For example: آب (âb) – water, اسب (asb) – horse, امید (omid) – hope, امشب (emšab) - tonight.
- ح (he) is also known as ه جیمی (he-jimi), and ﻩ (he) is also known as ه دوچش (he-docešma)
Persian Numerals

Note
The symbols for 4,5 and 6 are different from the standard numerals used for Arabic.
* All information was adopted from Omniglot website.






Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
All Comments (1)
Daniyal